HTTP status codes: What do they mean and why are they important for SEO?
HTTP status codes are short three-digit responses that a website server provides to a client’s browser in response to a request. Each http response code has its own meaning, and based on it, you can understand the state of the page and the problem (if any).
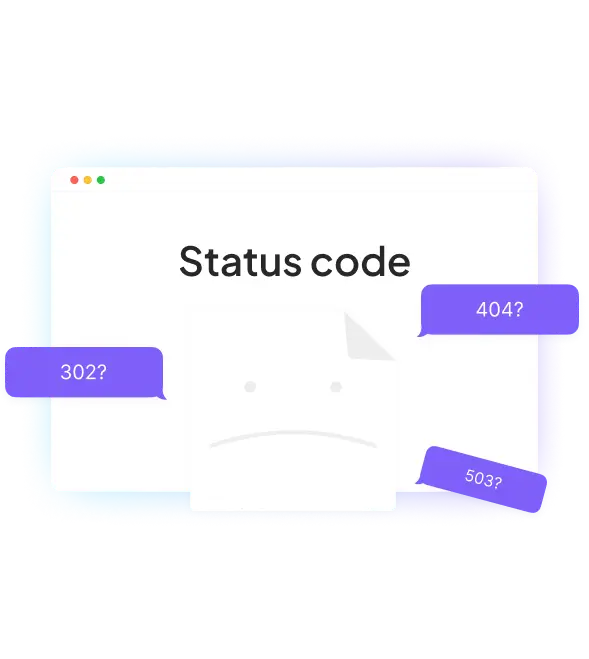




Main categories of HTTP status codes
1xx: Informational responses
These status codes indicate that the request has been received and is being processed.
- 100 Continue: The server has received the initial part of the request and the client should continue sending the rest of the request.
- 101 Switching Protocols: The client has requested a protocol switch and the server has not yet been confirmed.
2xx: Successful responses
These codes indicate that the client’s request was successfully received, understood, and accepted.
- 200 OK: The request was successfully completed. The most common code.
- 201 Created: The request was successfully completed and a new resource was created.
- 204 No Content: The request was completed successfully, but there is no content to send in response.
3xx: Redirect
These codes indicate that the client needs to perform additional actions to complete the request.
- 301 Moved Permanently: The resource has been moved to a permanent new URL. It is also called a 301 redirect.
- 302 Found: The resource is temporarily available at a different URL.
- 304 Not Modified: The resource has not been modified since the last request.
4xx: Client errors
These codes indicate that the problem occurred on the client side.
- 400 Bad Request: The server is unable to process the request due to a client error (e.g., syntax).
- 401 Unauthorized: The client must authenticate to receive the requested resource.
- 403 Forbidden: The server understands the request but denies access.
- 404 Not Found: The requested resource was not found on the server.
5xx: Server errors
These codes indicate that a problem occurred on the server while processing the request.
- 500 Internal Server Error: General server error.
- 502 Bad Gateway: The server received an incorrect response from another server.
- 503 Service Unavailable: The server is temporarily unavailable (usually due to overload or maintenance).


Why HTTP status codes are important

- Error diagnostics: HTTP status codes help developers quickly identify and fix problems.
- Improving UX: Proper use of status codes improves the user experience of a website by providing accurate and clear messages about the status of a request.
- SEO: Search engines use status codes to index content and determine page accessibility. For example, 301 redirects can preserve the SEO benefits of old URLs.
- Security: Correct status codes can protect resources from unauthorized access using 401 and 403 codes.

Increase visibility
for your business: SEO solution for growth!


How to check the HTTP status of the code
Checking the HTTP status of a code can be useful for developers, SEO specialists, and system administrators to diagnose problems and monitor the availability of web resources. There are several ways to check the HTTP access code status:
Using a web browser
Most modern browsers have built-in developer tools that allow you to check HTTP status codes. To do this, you need to:
- Open the web page you want to check.
- Right-click on the page and select “View Code” or press F12 to open the developer tools.
- Go to the Network tab.
- Refresh the page (“F5” or “Ctrl+R”).
- In the Network tab, you will see a list of requests. Click on a request to see details, including the error code.
Using online tools
There are many online tools that allow you to check the HTTP status code for web pages.
- HTTP Status Code Checker
- Web Sniffer
- Header Checker.
Simply enter the URL into the appropriate field on one of these sites and the tool will show you the HTTP status code and other response details of the required web page.


What are the most common http status codes and how do they affect SEO?
HTTP status codes play an important role in SEO because they affect how search engines index and rank web pages. Understanding how different status codes affect SEO will help you optimize your website and improve its visibility in search engines.
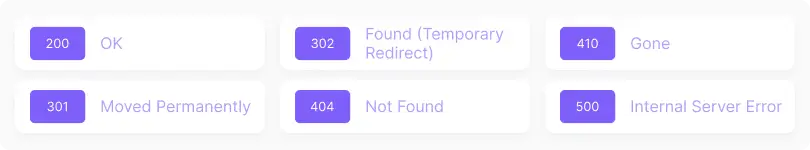
The main HTTP status codes and their impact on SEO
200 OK
- Meaning: This is the best result for web pages. When the server returns a 200 code, it means that the page is available and can be indexed by search engines. This has a positive effect on SEO because it indicates that the page is working correctly.
301 Moved Permanently
- Meaning: This code means that the page has been moved to a new permanent URL. Search engines transfer SEO weight from the old URL to the new one. Use 301 redirects when you permanently move content or change the URL structure. This helps to maintain your SEO rankings.
302 Found (Temporary Redirect)
- Meaning: This code indicates a temporary redirect. Search engines can continue to index the original URL, so using 302 redirects is not recommended for permanent changes. They can affect SEO if used incorrectly, as they do not convey full SEO weight.
404 Not Found
- Meaning: A 404 code means that the page was not found. Frequent 404 errors can have a negative impact on SEO, as they indicate that there are problems with the site. It is recommended to set up custom 404 pages that redirect users to other useful resources on your site to minimize the impact on SEO.
410 Gone
- Meaning: This code indicates that the page has been removed and is no longer available. Unlike the 404, the 410 code clearly tells search engines that the page was removed intentionally and they should remove it from the index. Using the 410 code can be useful for cleaning the index from old and unnecessary pages.
500 Internal Server Error Code
- Meaning: This code means that a general server error has occurred. Frequent 500 errors can greatly affect SEO as they indicate server issues. Search engines may perceive the site as unreliable if these errors occur frequently. If you constantly encounter 500 error code, it is advisable to move your site to a new hosting.
503 Service Unavailable
- Meaning: This code means that the server is temporarily unavailable, usually due to maintenance or overload. If you use the 503 code during maintenance, include the “Retry-After” header to tell search engines when to return. This helps to avoid negative SEO impact.

Increase visibility
for your business: SEO solution for growth!


Recommendations for optimizing status codes for SEO
Use the right redirects:
- Use 301 redirects for permanent URL changes.
- Avoid 302 redirects for permanent changes.
Monitoring errors:
- Check your website regularly for 404 and 500 errors.
- Use tools like Google Search Console to monitor errors and fix them in a timely manner.
Custom error pages:
- Create useful custom pages for 404 errors to direct users to other useful parts of your site.
Information for search engines:
- Use a “Retry-After” header for 503 errors during maintenance.
Index cleanup:
- Use the 410 code to remove unnecessary pages to keep the search engine index clean.


Conclusion
Error and status codes help you understand the state of the page and identify any errors. They indicate the server’s response to the user’s request. The 200 code is the most common, it indicates that the page is working properly. Other codes are not so common and each of them has its own unique meaning. To find out the status of the code, you need to go to the “F12” toolbar or check it through the Google Search Console.Also, these codes are very important for SEO, so it is better to contact SEObanda specialists to set them up correctly.
You may also like it

Brand identity: The key to brand recognition and SEO success
Every product has its own unique feature that sets it apart from other brands. It could be a special font, a unique mascot, or an interesting logo with the right...
What is a dynamic URL and its impact on SEO
A dynamic URL (Uniform Resource Locator) is a web address that changes depending on the user's request or specific parameters. It differs from a static
Press releases as an important part of your SEO strategy: Brand Push Services
SEO is the best promotion on the Internet that helps attract more potential clients and improve your market position. The use of press releases is an important SEO...